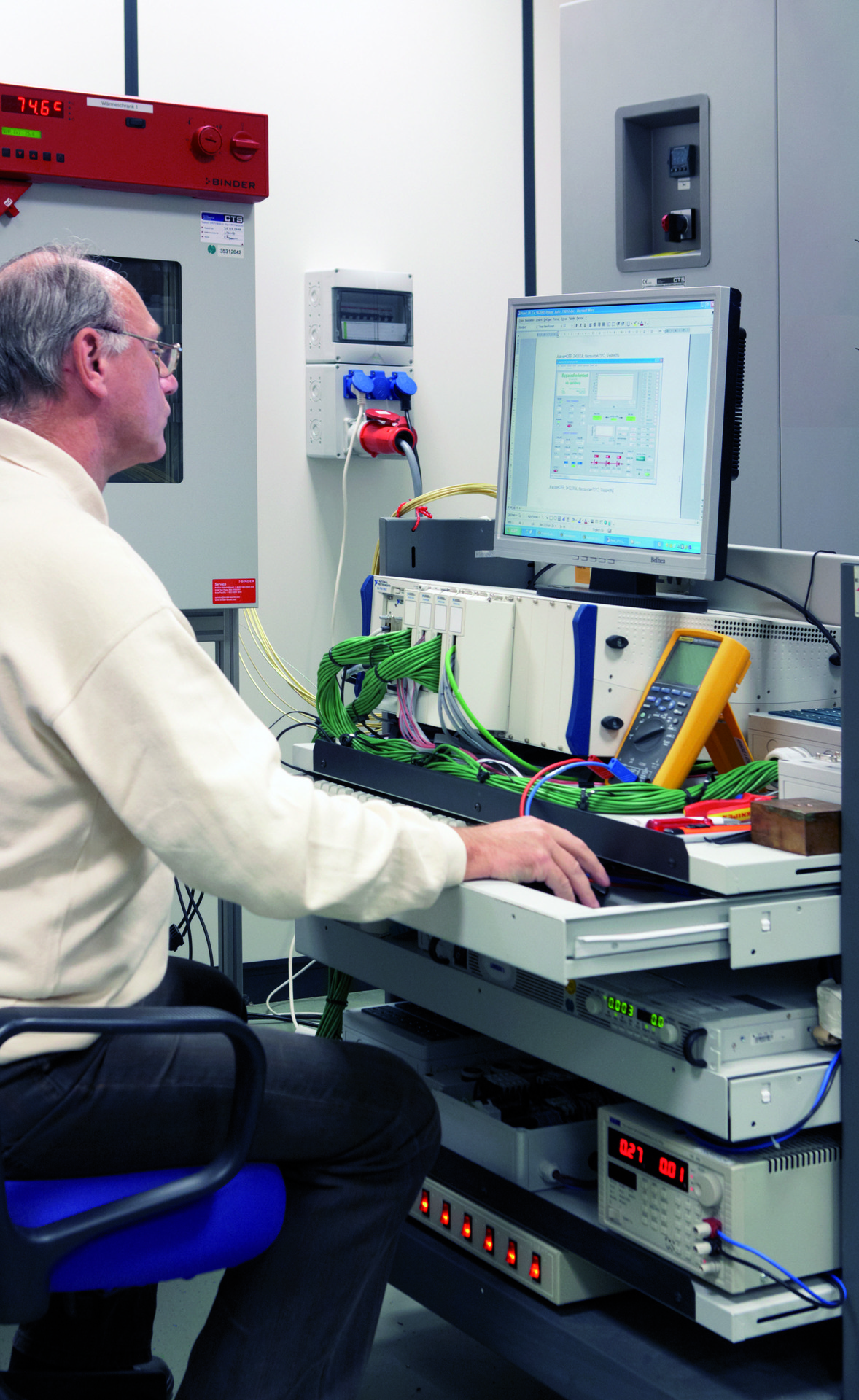
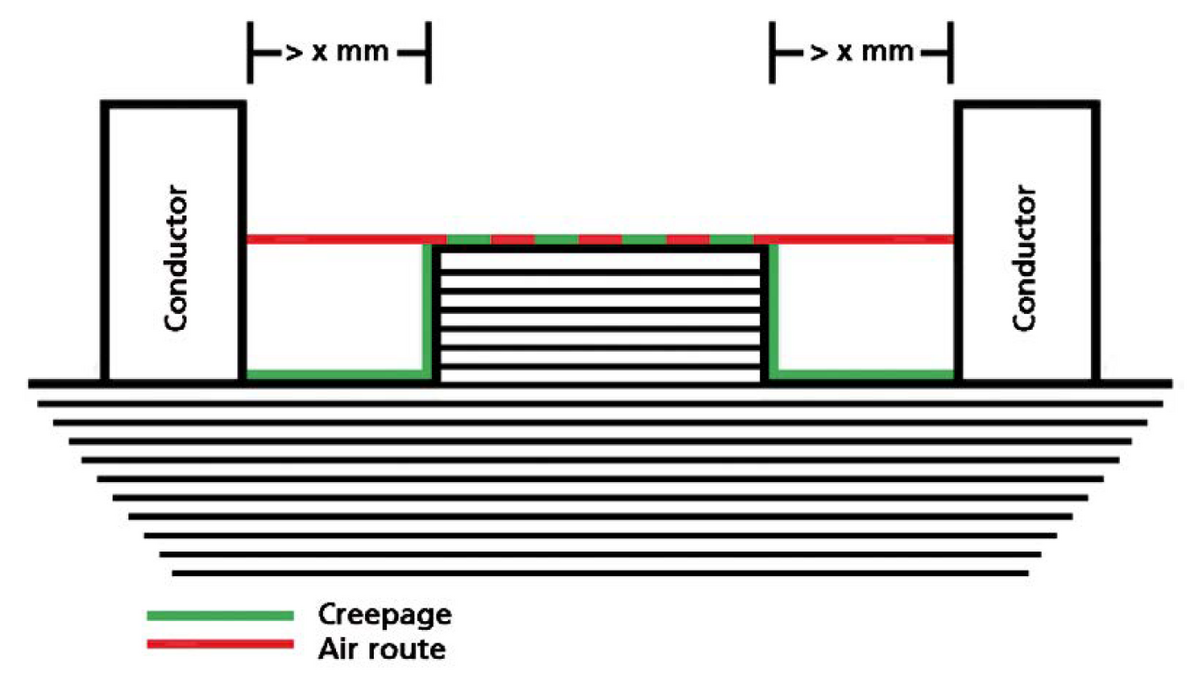
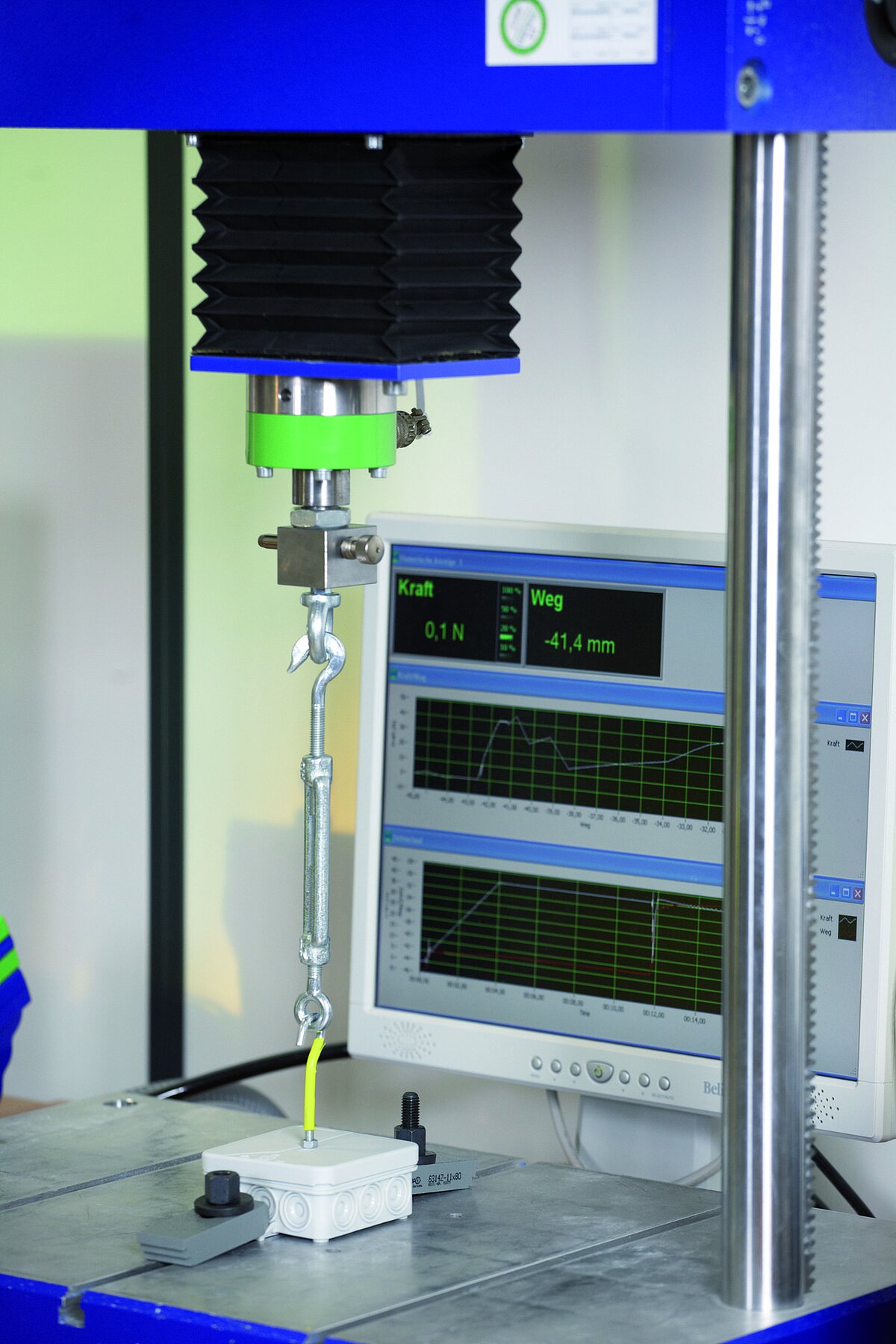
The mentioned tests are based on the following standards:
- DIN EN 60670-1 (VDE 0606-1),
- DIN EN 61439-1 (VDE 0660-600-1),
- DIN EN 62208 (VDE 0660-511)
with all associated amendments and extensions.
The tests described below are carried out, documented, analysed and evaluated there.
DIN EN 60670-1, VDE 0606-1
This standard applies for sockets, housings and housing parts for electrical installation equipment with a rated voltage of less than 1000 VAC and 1500 VDC, which are intended for household and similar fixed electrical installations both indoors and outdoors.
(DIN EN 60670-1, 1 Application Area)
DIN EN 61439-1, VDE 0660-600-1
This standard defines terms and specifies the operating conditions, construction requirements, technical characteristics and requirements for certification of low-voltage switch gear assemblies whose rated voltage is below 1000 VAC and 1500 VDC and which are movable or fixed.
(DIN EN 61439-1, 1 Application Area)
DIN EN 62208, VDE 0660-511
This standard applies for empty enclosures, as supplied by the manufacturer before any equipment is installed by the manufacturer of the switchgear assembly.
(DIN EN 62208, 1 Application Area)
Note:
Our in-house testing laboratory is certified according to:
- UL (Underwriters Laboratories)
- DIN EN 60670-1, 60670-22, 60529
The tests described below are carried out, documented, analysed and evaluated there.


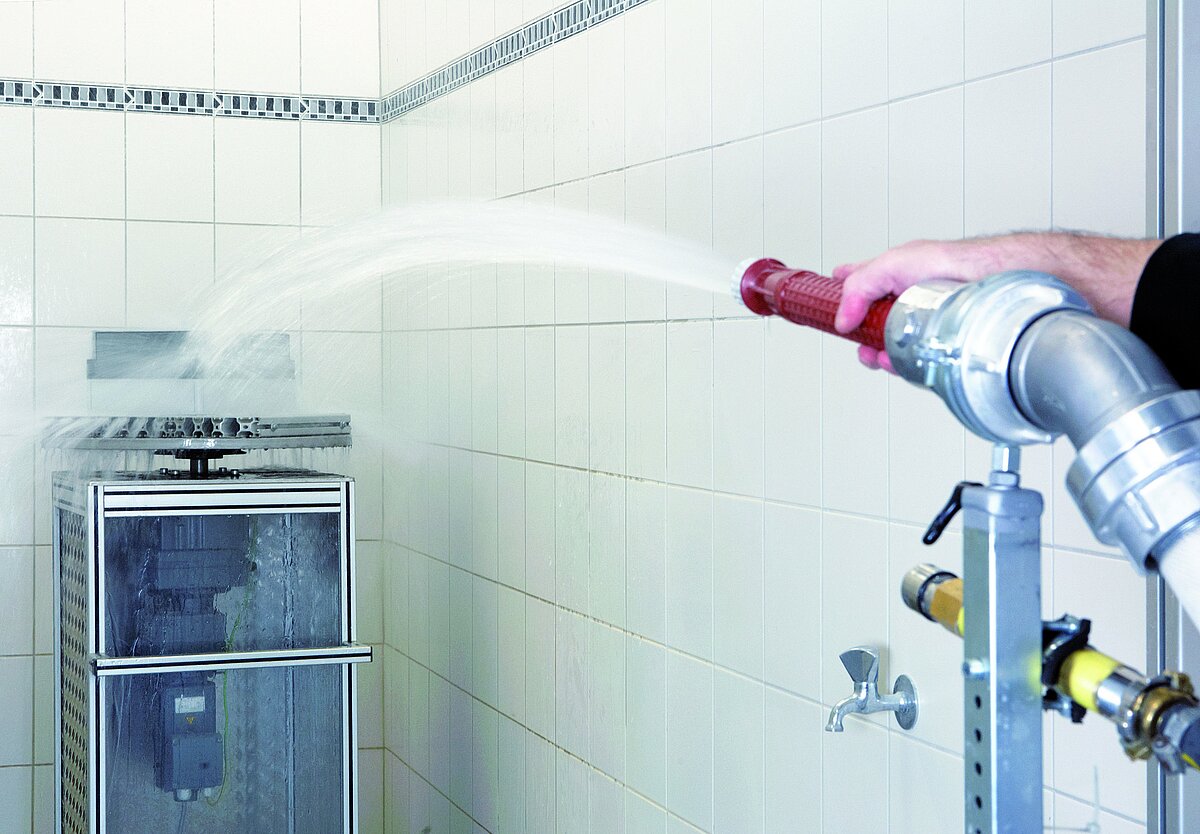
![[Translate to English - International:] Prüfsonden nach DIN EN 60529](/media/_processed_/a/6/csm_Prufsonde_73c8b76f86.jpg)


![[Translate to English - International:] Start der Prüfung](/media/_processed_/4/7/csm_088_7be7d2e430.jpg)
![[Translate to English - International:] Ende der Prüfung](/media/_processed_/e/3/csm_098_f9351bacbc.jpg)